
Forests for the future
Shambavi Awasthi
(Banda University of Agriculture & Technology Banda U.P. (210001))

“A famous quote in Sanskrit was – “One stepwell is equal to ten wells, one pond is equal to ten stepwells, one son is equal to ten ponds and one tree is equal to ten sons.”
Why do we need forests?
Forest is vital for sustaining life on Earth, covering approximately one-third of the planet’s land. Their destruction not only impacts the environment but also affects people’s lives, homes, and livelihoods. Furthermore, forests play a crucial role in addressing biodiversity and climatic crises.
Importance of forests
1. For mother earth
Forests are star crucial for biodiversity, as they are home of terrestrial biodiversity, including a significant percentage of various animals’ species. Deforestation could almost result in a loss of up to one hundred species daily, making it imperative to halt forest to prevent further biodiversity decline. When forest is cleared, the entire ecosystem is disrupted, leading to severe consequences for all. It provides habitats for iconic species like tigers, giant pandas, gorillas, and orangutans. The clearance of forested areas for multiple purposes is a primary driver of habitat and biodiversity loss.
2. For people
Forest is crucial to human well-being, with over a billion people relying on them for sustenance and resources. They provide oxygen, shelter, and employment, while also playing a vital role in preventing erosion and maintaining water quality. Deforestation due to rise in population not only impacts those people who are directly dependent on forest but also increases the risk of diseases crossing over from animal to humans. On the other hand, spending time in the forest has been linked to various health benefits, from cardiovascular health to mental wellbeing.
3. For Climate change
Forests play a crucial role in mitigating climate change by absorbing and storing carbon emissions. Their destruction releases large amounts of carbon, contributing to the climate crisis. In addition to mitigating the effects of climate change-induced events such as wildfires can hinder the regenerative capacity of forests. Therefore, it is essential to halt deforestation and restore forests to combat climate change effectively.
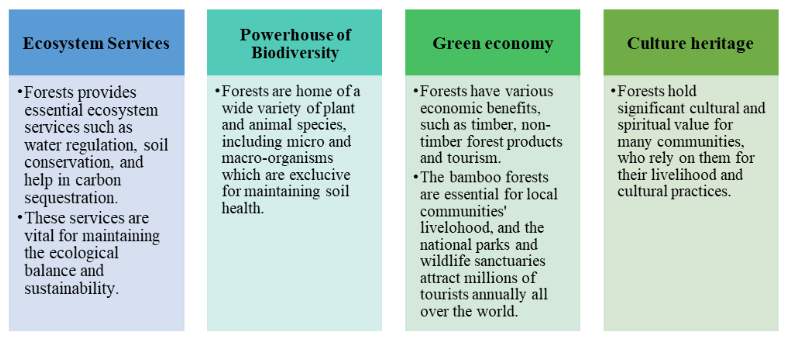
Fig:1 Significance of forests for the future
Challenges to build resilience forests
- Deforestation- Forests are threatened by illegal logging, mining, and land convention for agriculture and urban development, leading to deforestation and land degradation. These activities have negative impacts on the environment and the communities relying on forests for their livelihoods.
- Climate change- Forest disturbances, such as insect outbreaks, invasive species, wildfires, and storms, are reducing forest productivity and altering species distribution due to climate change.
- Unregulated grazing- The lack of a strict grazing regulatory framework has led to overgrazing in various parts of the world, causing severe damage to forests.
- Resource conflict- There is often conflict between local communities and commercial interests, leading to social tensions and violence as diverse groups struggle to access and use forest resources.
Way Forward
- Community management program- A network of community-managed forests is being developed to give local communities the responsibility for protecting and managing their forests. This approach aims to empower local people and involve them in the conservation of their forests. Direct engagement with communities can transform the informal forest economy into fair and transparent business transactions, incentivizing protection, management, and restoration of forests.
- Innovative reforestation- In recent reforestation efforts, must include innovative methods that have been employed to accelerate the process while drones are being used to keep planting trees. Additionally, the Miyaki technique for forest regeneration can be utilized. These advancements aim to contribute to global reforestation efforts.
- Innovations in education- Early childhood initiatives include teaching outdoors, nature walks, and curriculum-based outdoor experiments. These efforts aim to engage children in forest care through unique practices like using seed pencils and seed balls.
- Waste to wealth– Forest waste can be turned into valuable resources through technology, reducing and recycling enormous quantities of inferior wood dumped in forests. Seasoning and prevention treatment can improve its use, and promoting standards and codes for wood products can enhance their quality and value.
- Approach towards Natural-based solutions- Nature-based solutions, including blue-green infrastructure like green roofs, rain gardens, and constructed wetlands, play a crucial role in mitigating the impacts of climate change. These solutions capture CO2 from the air and store it in plants, soils, and sediments. Additionally, they support the regeneration of forests and the restoration of wetlands.
Conclusion
Forest plays a crucial role in mitigating climate change by absorbing carbon emissions and providing protection against extreme weather events. Additionally, forests provide essential ecosystem services, economic benefits, and cultural and spiritual value for various communities. Therefore, it is imperative to halt deforestation and restore forests to ensure the sustainability of life on earth.


